QCHALLenge Project Completion
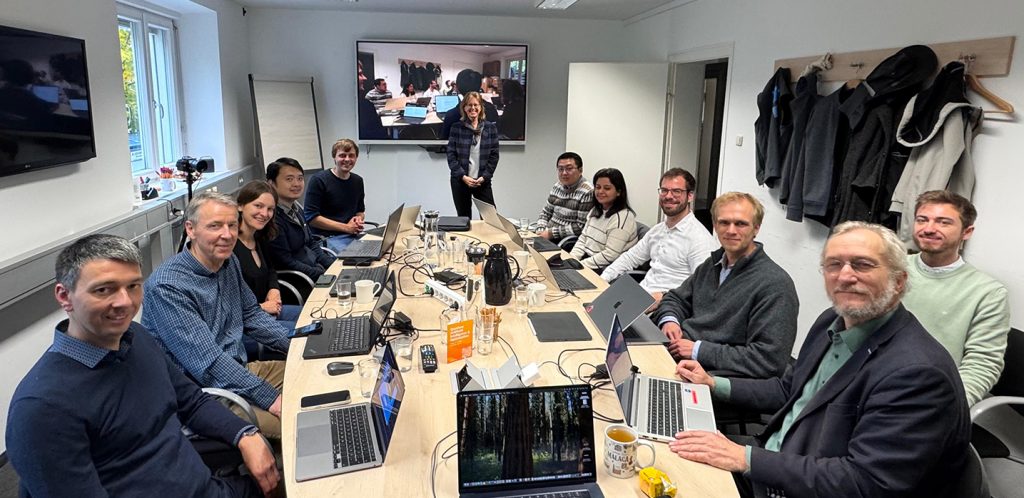

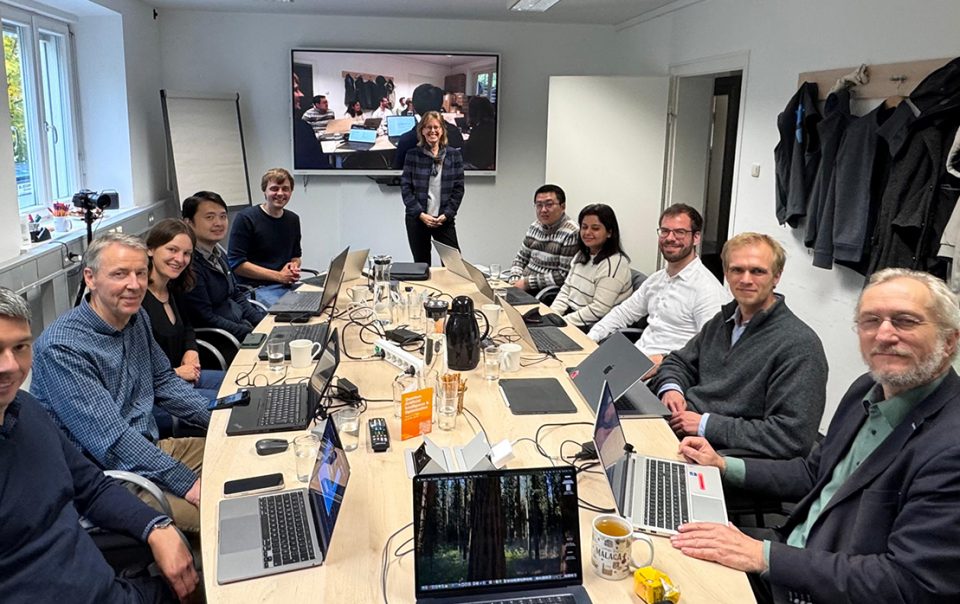
Final Consortial Meeting in Munich
(Munich, 09.10. 2025) After three years of close collaboration with our partners BASF, BMW, SAP, and Ande Semiconductor, supported by Aqarios as part of the BMFTR-funded QCHALLenge project, we proudly presented our final results at the closing meeting with DLR-PT on October 9th, 2025.
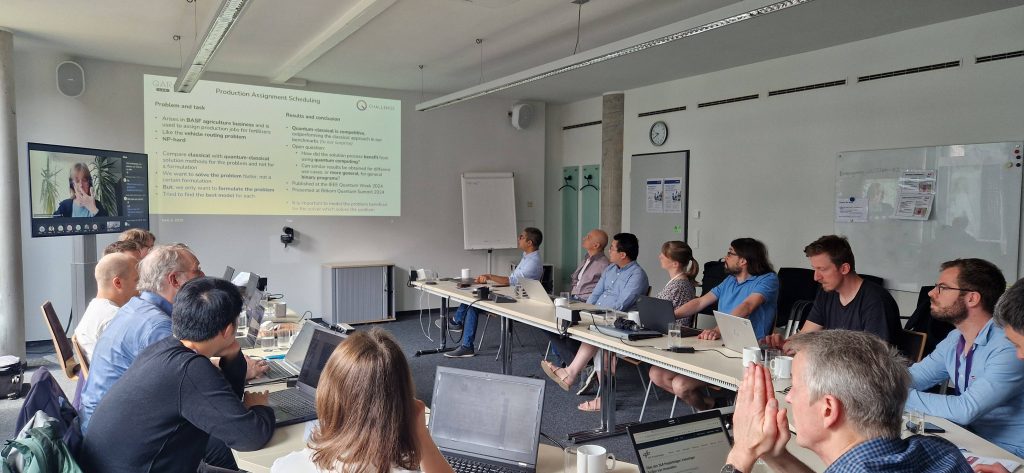
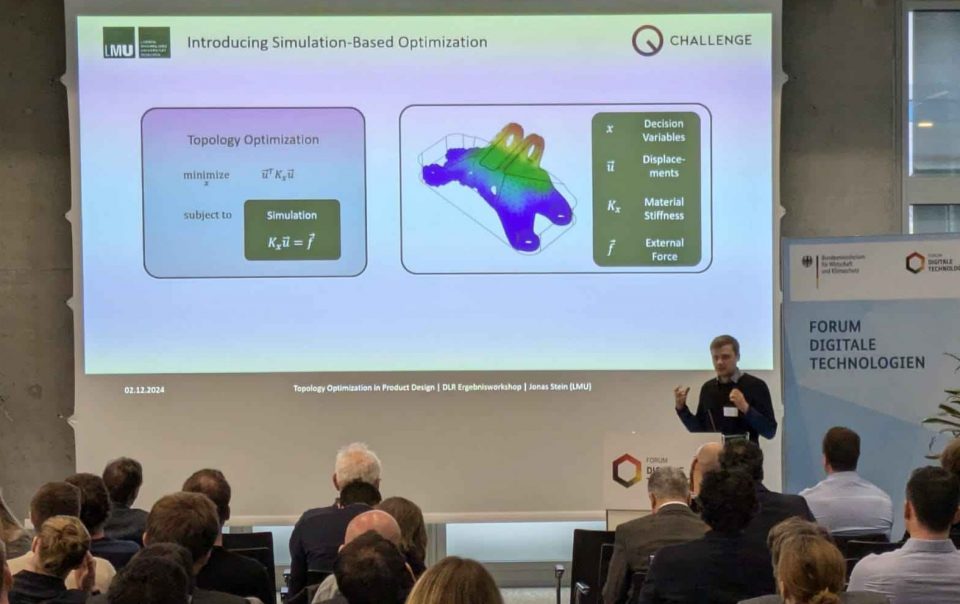
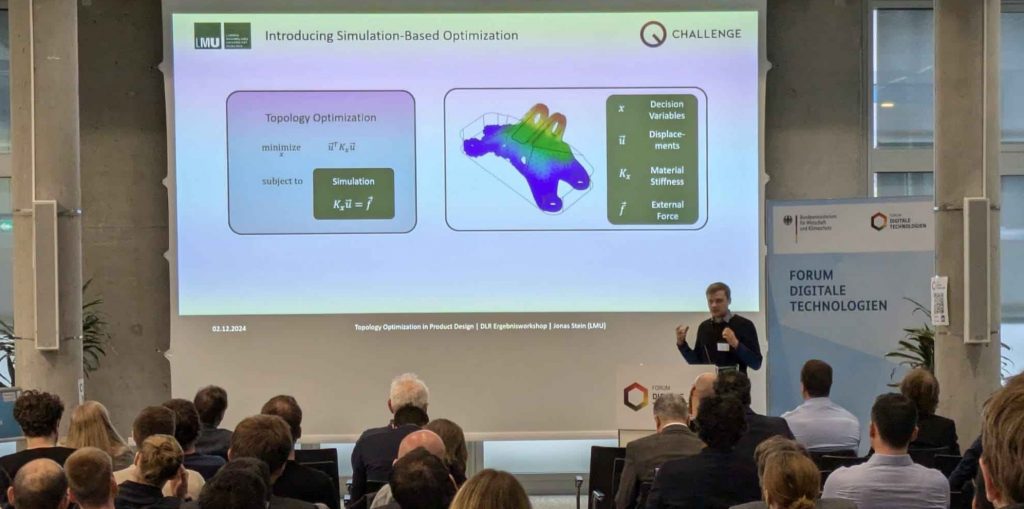
Leading this collaboration has been an extraordinary experience – one that started with the QC Optimization Challenge hosted by the QAR-Lab and evolved into one of the most comprehensive joint efforts on industrial quantum applications to date. Together, we explored more than a dozen truly real-world use cases contributed by our industry partners – ranging from production scheduling and sensor placement to train routing and resource optimization. Through this, we achieved significant progress in bridging the gap between quantum research and industrial practice. In over 30 scientific publications, we developed and refined methodologies to apply quantum algorithms to real optimization problems in production and logistics – benchmarked on five different (quantum-inspired) computers. To ensure that quantum solutions can be used seamlessly in today’s industrial automation ecosystems, we created an open source software-framework enabling uniform access to multiple use cases.
To support the quantum readiness of industry, we summarized all findings in a quantum roadmap that provides clear recommendations on when and where quantum computing can offer tangible advantages in the future.
Building on these results, we are now looking forward to integrating the QCHALLenge Framework into the QuCUN Ecosystem and Munich Quantum Software-Stack and beyond – in collaboration with tools like Aqarios Luna and Quark. A heartfelt thank you to all partners and contributors for making this ambitious journey possible – and for proving that collaboration between academia and industry can truly accelerate the path toward Quantum Advantage in Industry.