Q-Grid - Application of quantum computers for the optimization of future energy grids
About this Project
The Q-Grid research project aimed to explore the potential of quantum computing for optimizing future decentralized energy grids. The focus was on developing novel quantum-based and quantum-inspired optimization algorithms for complex, combinatorially difficult problems in the energy sector. To this end, various use cases – such as microgrid formation, dynamic pricing, and cost allocation in peer-to-peer markets – were converted into QUBO models and tested on real and simulated quantum hardware. Intelligent preprocessing, algorithmic innovations, and hybrid solution approaches were used to evaluate the practical suitability of quantum-based methods. The goal was to obtain a reliable assessment of the extent to which quantum computing can contribute to the efficiency, resilience, and sustainability of energy networks in the future.
Our Consortium

LMU Munich is acting as consortium leader in the project, taking on the majority of the project management. As a research institution with many years of expertise in the field of quantum computing (LMU is, among other things, a founding partner of PlanQK), LMU provides support in all research-intensive work packages. As a university research group, LMU’s QAR-Lab plans to utilize the project results in teaching, scientific publications, and funding and research projects based on Q-Grid.
E.ON Digital Technology GmbH is one of Europe’s largest energy companies, headquartered in Essen, Germany, and focuses on energy networks, sustainable power supply, and customer-oriented energy solutions. E.ON Digital Technology GmbH is the central IT and digital company of the E.ON Group and is responsible for the development, integration, and operation of digital systems and technologies within the group.
The Aqarios GmbH is a Munich-based technology company focused on quantum computing that develops software tools and algorithms for quantum-assisted optimization.
Project Results
The Q-Grid project demonstrated the potential of quantum computing for optimizing future, highly complex decentralized energy grids.
The focus was on three practical use cases: dynamic pricing, the formation of self-sufficient energy communities, and cost allocation in peer-to-peer markets. Using the semi-symmetry approach, LMU developed a novel preprocessing method for QUBO problems that significantly reduces coupling density and circuit depth. This allowed quantum and hybrid algorithms to be used more efficiently and with greater error resistance. BOX-QUBO is a universal optimization workflow that automatically learns QUBO formulations and makes them reusable. Building on this, Learning QUBO Formulations from Data is an AI-based approach that generates optimization models directly from data.
Together with E.ON and Aqarios, problem-specific decomposition methods were developed that split large optimization tasks into subproblems suitable for quantum hardware. This decomposition enabled realistic simulations with several thousand customers and complex network structures for the first time. In the discount scheduling use case, the hybrid LeapHybridCQM solver outperformed classical solvers in terms of both solution quality and fairness of price distribution for 200 or more customers. The self-reliant community detection problem enabled the identification of self-sufficient energy communities with up to 1888 nodes; hybrid quantum approaches showed the best results here. For the coalition formation of prosumers, quantum annealing on D-Wave hardware showed more favorable scaling behavior than classical methods and QAOA on IBM systems. The third scenario—cost distribution in P2P markets—proved, however, that convex problems continue to be dominated by classical optimizers such as Gurobi. An extended QAOA method with XY mixers and indicator functions was able to efficiently integrate complex constraints into quantum circuits and showed significant performance gains in simulations.
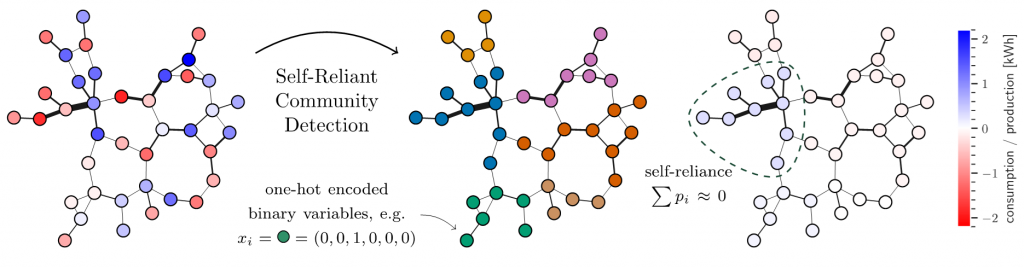
Example of a power grid with prosumers and consumers. Negative values refer to generation, positive values to consumption. The line thickness indicates the absolute power flowing through this line. The community of each node is described by the one-hot encoding of K binary variables. Net consumption within a community should be minimized to ensure self-sufficiency. (Figure taken from Bucher et al. 2024)
The methods developed are widely applicable and can be transferred to other areas such as logistics, finance, and energy storage management.
Overall, Q-Grid confirmed that hybrid and quantum-inspired optimization approaches already offer practical advantages today and can play a key role in the energy transition as hardware development progresses.
Publications
Nüßlein, J., Roch, C., Gabor, T., Stein, J., Linnhoff-Popien, C., & Feld, S. (2023, July). Black Box Optimization Using QUBO and the Cross Entropy Method. In International Conference on Computational Science (pp. 48-55).
Nüßlein, J., Sünkel, L., Stein, J., Rohe, T., Schuman, D., Feld, S., O’meara, C., Cortiana, G., & Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2025). Reducing QUBO Density by Factoring out Semi-Symmetries. In A. P. Rocha, L. Steels, & H. J. van den Herik (Eds.), Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 1, pp. 783-792). (International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence). SciTePress. https://doi.org/10.5220/0013395900003890
Nüßlein, J., Schuman, D., Bucher, D., Mohseni, N., Ghosh, K., O’Meara, C., … & Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2024, September). Towards Less Greedy Quantum Coalition Structure Generation in Induced Subgraph Games. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE) (Vol. 2, pp. 28-33). IEEE Computer Society.
Nüßlein, J., Zielinski, S., & Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2025, June). Learning QUBO Formulations from Data. In International Conference on Innovations for Community Services (pp. 209-227). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
J. Nüßlein, M. Zorn, F. Ritz, J. Stein, G. Stenzel, J. Schönberger, T. Gabor, and C. Linnhoff-Popien, „Optimizing Sensor Redundancy in Sequential Decision-Making Problems“, in Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART ‘25), pp. 245-252, 2025.
Kölle, M., Topp, F., Phan, T., Altmann, P., Nüßlein, J. and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2024). Multi-Agent Quantum Reinforcement Learning Using Evolutionary Optimization. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence – Volume 1: ICAART; ISBN 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN 2184-433X, SciTePress, pages 71-82. DOI: 10.5220/0012382800003636
Blenninger, J., Bucher, D., Cortiana, G., Ghosh, K., Mohseni, N., Nüßlein, J., … & Wimmer, B. (2024). Q-grid: quantum optimization for the future energy grid. KI-Künstliche Intelligenz, 38(4), 339-349.
Bucher, D., Porawski, D., Wimmer, B., Nüßlein, J., O’Meara, C., Mohseni, N., … & Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2024). Evaluating quantum optimization for dynamic self-reliant community detection. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid.
Bucher, D., Kraus, N., Blenninger, J., Lachner, M., Stein, J., & Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2024, September). Towards Robust Benchmarking of Quantum Optimization Algorithms. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE) (Vol. 3, pp. 159-170). IEEE Computer Society.
Mohseni, N., Morstyn, T., O’Meara, C., Bucher, D., Nüßlein, J., & Cortiana, G. (2025). Demonstrating Quantum Scaling Advantage in Approximate Optimization for Energy Coalition Formation with 100+ Agents. Quantum Science and Technology.
Contact
Please direct inquiries to the consortium to:
E-Mail: qar-lab@mobile.ifi.lmu.de
Telefon: +49 89 2180-9153
QAR-Lab – Quantum Applications and Research Laboratory
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
Oettingenstraße 67
80538 München

Website of Project Organizer
Copyright © Q-Grid | 2022 – 2025

